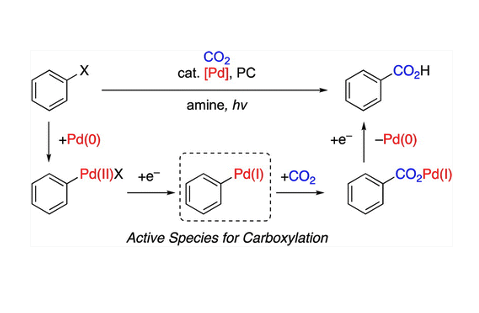
The reaction mechanism of palladium-catalyzed visible light-driven carboxylation of aryl halides and triflates with a photoredox catalyst was examined in detail. Experimental and theoretical studies indicated that the active species for photoredox-catalyzed reduction was cationic ArPd(II)+ species to generate nucleophilic ArPd(I) or its further reduced ArPd(0)− species, which reacted with CO2 to give carboxylic acids. Hydrodehalogenated compounds, main byproducts in this carboxylation, were thought to be generated by protonation of these reduced species.