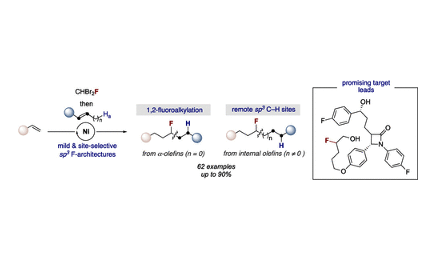
A catalytic monofluoroalkylation of terminal and internal olefins is described. This protocol is distinguished by its mild conditions, wide scope─including the utilization of chemical feedstocks and advanced intermediates─and exquisite site-selectivity for both α-olefins and internal olefins. In the latter, C–C bond formation occurs at remote sp3 C–H sites, thus unlocking a blueprint for incorporating monofluorinated alkyl chains that complements existing techniques occurring at sp3 centers.