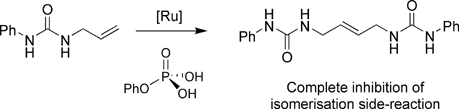
A systematic study of the ruthenium-catalysed metathesis of alkenes containing hydrogen-bonding substituents (namely urea and thiourea groups) is presented. Under standard metathesis conditions, several of the substrates under study undergo alkene isomerisation instead of the targeted metathesis. However, in the course of these investigations it has been established that this unwanted isomerisation process can be suppressed by addition of phenylphosphoric acid to the reaction mixture. Some other potential isomerisation inhibitors (e.g. benzoic acid and salts of phosphoric acid) have been studied and their performance compared to that of phenylphosphoric acid. To extend the scope of phenylphosphoric acid, we also studied the metathesis of 1,3-diallylurea. Interestingly, not only did we observe the complete suppression of the isomerisation process, but also that it is possible to obtain instead of the ring-closing metathesis (RCM) product, ADMET oligomers resulting from the cross-metathesis of diallylurea at higher concentrations.