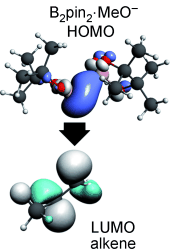
A nucleophilic sp2 carbene-type boryl moiety, formed upon interaction of tetraalkoxydiboranes and a Lewis base, can attack non-activated C=C bonds. Computational studies identify the interaction as the overlap between the strongly polarized B-B σ bond (HOMO) and the antibonding π* orbital (LUMO) of the C=C bond. Conceptually, the normally electrophilic boron becomes nucleophilic and forces the olefin to act as an electrophile.