The Material Characterization Unit provides support to ICIQ researchers working on heterogeneous catalysis (gas phase reactions catalyzed by solids).
To this purpose, it comprises equipment for a wide catalyst characterization and testing, including textural and reactivity studies, performance of the catalysts for different reactions at different operating conditions and mechanism elucidation of catalytic processes.
The following techniques are available:
- Physisorption for solids textural characterization (porous structure).
- Chemisorption
- Helium pycnometry for the real density of solids.
- Temperature programmed reaction (TPD/TPR/TPO, pulse chemisorption) for surface reactivity studies.
- Steady state catalytic activity studies in a fixed bed reactor.
- Reactor TAP for the elucidation of reaction mechanisms.
- MS and GC for the on line analysis of gas streams and atmospheres.
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) for the measurement of hydrodynamic size and zeta potential of nanoparticles and macromolecules in suspension.
Equipment
-
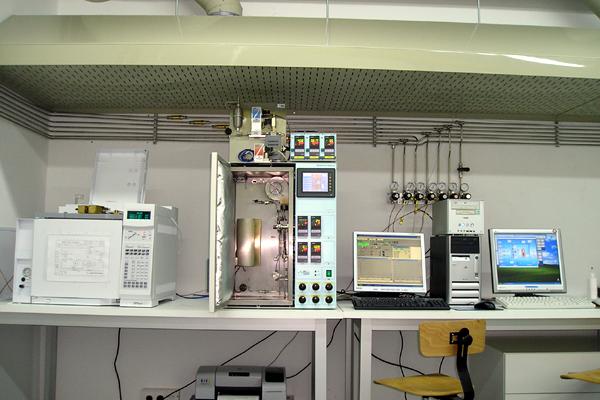
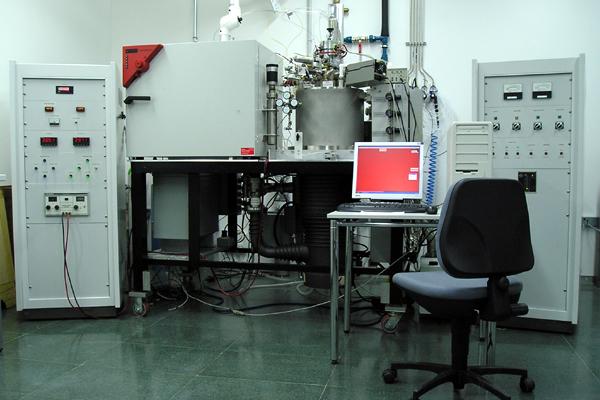
Catalytic activity reactor
A compact apparatus for catalytic activity experiments (Microactivity Reference by PID Eng&Tech), including a 9.2 mm I.D. reactor, temperature control (up to 1000 ºC) and pressure control (up to 100 bar). It is possible to work with up to five different gases and a vapour. The outlet gas flow is analyzed by a GC (G1540N by Agilent), with TCD and FID detectors in parallel. -
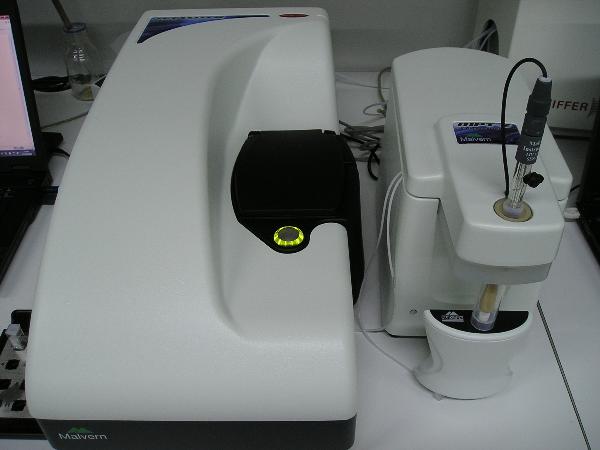
DLS for nanoparticles
Malvern nanoZS for zeta potential and hydrodynamic size of nanoparticles and macromolecules by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). Further, pH or certain additives influence in these properties can be studied with the MPT-2 autotitrator, allowing for example the isoelectric point determination. Molecular weight can be estimated in DLS experiments or it can be measured by Static Light Scattering (SLS), provided the refractive index increment with the concentration is known. -
Mass Spectrometer II
It is a newer version of OmnistarTM by Pfeiffer, but with similar features: the mass analyzer is a quadrupole and the sampling system consists on a heated steel capillary for the on-line analysis of gas atmospheres or streams. -
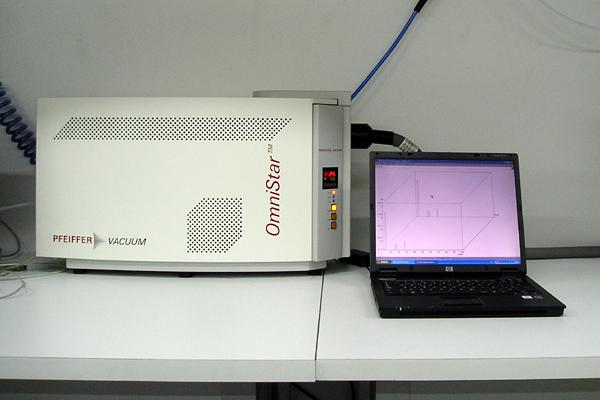
Mass spectrometer
It is an OmnistarTM by Pfeiffer, the mass analyzer being a quadrupole and the sampling system consisting on a heated capillary to the on-line analysis of gas atmospheres or streams. -
Physi&Chemisorption Analyzer
Physisorption is an unspecific weak gas-solid interaction below the critical temperature of the gas that occurs throughout the solid surface. It allows obtaining textural information like surface area, pore size distribution, pore volume, etc. This model (Autosorb iQ by Quantachrome) can reach high vacuum, allowing the analysis of microporous materials (pores smaller than 2 nm). Chemisorption is a strong specific interaction that affects only the surface parts occupied by atoms that can chemically interact with the gas. It allows determining the amount of surface active positions, and derived magnitudes like the dispersion of the active phase. -
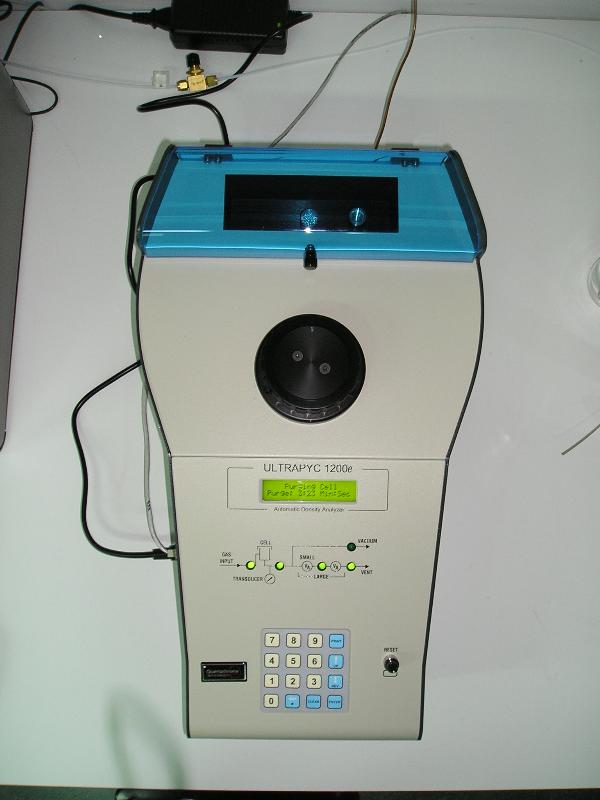
Pycnometer
It measures the skeletal or true density of solids by He displacement (micro-Ultrapycnometer 1200e by Quantachrome). -
TAP-2 reactor
Catalytic microreactor (Mithra Technologies) implemented with a mass spectrometer located just at the reactor outlet; in such a way that it is even possible to detect medium-large average lifetime intermediates (from 1 ms). Although it can run in a continuous flow mode, at atmospheric or higher pressure, its main feature is the capability of working with gas pulses in high vacuum conditions. This, combined with the possibility of using isotopic labels, makes the TAP-2 system one of the most powerful tools in the study of reaction mechanisms and the obtaining of kinetic parameters. -
TPD/TPR/TPO
This apparatus (TPDRO 1100 by Thermo Fisher) allows studying the interaction of a solid sample in contact with a reactive gas, obtaining the different sorts of active sites and their importance in quantitative terms. To this purpose, different temperature programmed reactions can be carried out, namely reduction (TPR), oxidation (TPO), and desorption (TPD) of a compound that previously has saturated the sample. Additionally, pulse chemisorption experiments can be conducted, in this case at constant temperature.